Key Takeaways
- Comprehensive threat data is critical for anticipating and mitigating cyberattacks.
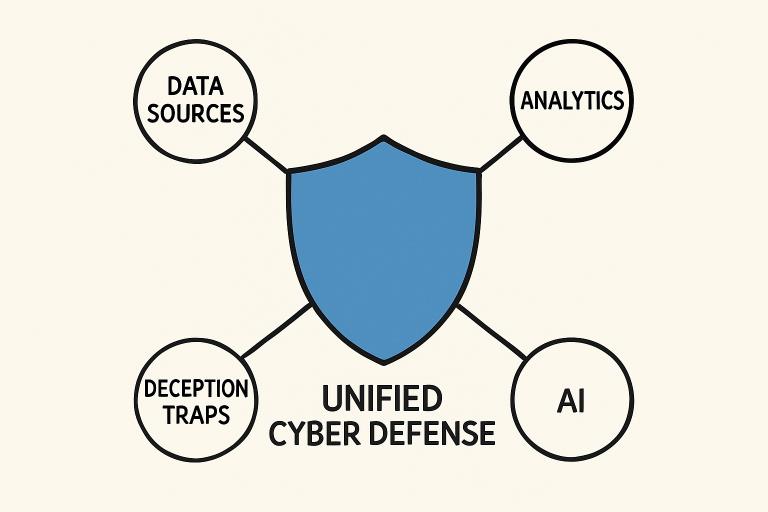
- Modern cyber defense relies on a combination of technologies, including Threat Intelligence Platforms, predictive analytics, deception tools, and Zero Trust Architecture.
- Staying ahead of evolving threats, especially those powered by AI, requires an adaptive, intelligence-driven approach.
- Operationalizing threat intelligence helps streamline detection and response efforts, thereby strengthening protection.
Understanding Threat Data
As digital threats continue to grow in sophistication and scale, organizations must rely on actionable intelligence to prevent security breaches and mitigate attacks. Threat data refers to information gathered on cyber risks, such as malware signatures, attack techniques, threat actors, and security vulnerabilities, collected from internal monitoring, open web sources, and commercial solutions. This deep insight is essential for organizations to detect and neutralize threats before significant damage occurs.
Threat data enables security professionals to quickly identify potential weaknesses in their infrastructure. To operationalize this data for real-world scenarios, organizations turn to threat detection software that not only aggregates disparate threat indicators but also synthesizes actionable reports. By recognizing recurring attack patterns or anomalous behavior, enterprises can prioritize defense tactics and proactively protect sensitive assets.
The value of threat data is amplified through context; for example, linking a phishing campaign with specific malware strains or known criminal groups. This correlation helps incident response teams prioritize their actions and allocate defenses where they are needed most.
A critical part of any cyber defense strategy is aligning threat intelligence with organizational risk, ensuring security investments are both efficient and effective. The successful operationalization of threat intelligence hinges on this alignment, which transforms raw data into meaningful security actions.
The Role of Threat Intelligence Platforms
Threat Intelligence Platforms (TIPs) are designed to collect, aggregate, and analyze threat data across a wide spectrum of sources. These tools power real-time decision-making by correlating threat indicators, automating response playbooks, and helping organizations adapt to new tactics deployed by cybercriminals. TIPs streamline threat intelligence management and enable security teams to track sophisticated threat campaigns more efficiently.
TIPs can integrate with other tools in a security stack, such as Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) systems or endpoint protection systems, enabling coordinated, rapid responses to unfolding attacks. By tracking threats in real time and prioritizing those most relevant to an organization’s unique risk profile, TIPs close the gap between detection and response, reducing the time criminals have to inflict damage.
Enhancing Detection with Predictive Analytics
Predictive analytics harnesses large volumes of historical and real-time threat data to uncover emerging risks before they materialize. These analytics use machine learning algorithms to detect behavioral anomalies, flag unauthorized access attempts, and anticipate ransomware attacks by recognizing early warning signs. Predictive analytics empowers organizations to defend against future attacks, not just those already identified in the wild.
By forecasting threats and continuously updating risk models, predictive analytics enables security teams to move from reactive postures to proactive defense, minimizing dwell time and improving organizational resilience.
Implementing Deception Technology
Deception technology introduces decoys, traps, and lures throughout a network to attract and mislead attackers. When adversaries interact with these false assets, security teams receive immediate alerts of suspicious activity, providing valuable insights into the attacker’s goals, tools, and methods.
Effective deception strategies not only disrupt ongoing attacks but also gather intelligence on advanced threats, a crucial step in defending against persistent adversaries who evade conventional detection. Deception solutions operate unobtrusively, minimizing risk to production systems while providing actionable threat data that enhances future defenses.
Adopting Zero Trust Architecture
The Zero Trust model is predicated on the idea that no user or device, inside or outside an organization’s perimeter, should be inherently trusted. Every access attempt must be continuously authenticated and authorized based on identity, context, and policy. This approach sharply curtails the impact of credential theft, lateral movement, or insider threats.
In contemporary cyber defense, Zero Trust aligns closely with the principle of least privilege, giving users only the access necessary for their role. This architectural shift is touted by many experts as a foundational best practice for reducing breach risks in complex IT environments.
Addressing AI-Driven Threats
With the rapid proliferation of artificial intelligence, attackers now deploy AI-derived tactics such as deepfake phishing, automated vulnerability scanning, and malware that adapts in real time to evade detection. Defending against these advanced threats demands adaptive, intelligence-driven defenses that leverage automation and threat modeling.
Integrating AI into security operations, both for automated detection and investigation, helps security teams keep pace with adversaries. The fight against AI-augmented threats is an arms race that will continue to intensify, reinforcing the necessity for continuous investment in threat intelligence and machine-speed response.
Integrating Threat Data into Defense Strategies
Building a modern defense posture requires seamlessly integrating threat intelligence into daily security workflows. This includes aggregating and contextualizing data via TIPs, applying predictive analytics to anticipate threats, and employing technologies such as deception and Zero Trust to harden network defenses.
- Utilize Threat Intelligence Platforms for real-time, actionable insights.
- Apply predictive analytics to proactively identify and neutralize threats.
- Implement deception technology to catch stealthy adversaries and analyze attacker behavior.
- Adopt Zero Trust Architecture to mitigate insider threats and enforce strict access controls.
- Continuously adapt defenses by monitoring and countering AI-driven threats.
These measures create a unified, intelligence-led defense that positions organizations to repel both current and emerging digital dangers.
Conclusion
As cyber threats become more dynamic and malicious actors embrace technological innovation, relying on timely and comprehensive threat data is no longer optional it is essential. Organizations that operationalize threat intelligence, deploy advanced analytics, integrate deception defenses, and enforce Zero Trust principles emerge resilient, capable, and ready to counter the evolving threat landscape.